

 |
|
 |
|
|
I adore Google. Period. I use it each time I need to search some stuff
on the Net and it turns up the most wondrous results so I was truly
happy to know that there is something better than Google ... Google
Guide! Yep, it teaches you all the tips and tricks ... so you'll be
able to search even better! Thank God for Google Guide!
|
|
|
Great site! You've maintained the elegant simplicity of Google's own site, along with a thorough attention to detail and content.
--sublime1-ga, Google Answers Researcher
|
|
|
Excellent tutorial for both new/experienced Google users.
|
You can make your website (more) popular and generate (more) income. Learn how in this segment, which provides tips on:
The information in this section is based on my experience in designing and developing Google Guide, which is now the top result for the queries including:
Note: There are thousands of sites devoted to developing a website and optimizing its performance. So, should you want more detailed information, just search for it. But be careful: there are sites that charge good money for bad information.
Want to give a presentation on developing a website or print the files in this segment of Google Guide? Then check out the links below.
| Creating Content for Your Website |
Following each tip on creating content is information about how I developed Google Guide and improved its content.
The goal of Google Guide is to make searching even easier for novices and experienced users.
Nelson Blachman, my father, is blind and is a wonderful reviewer and beta tester for Google Guide.
Studying Google Guide logs, I've learned which pages are most popular among users and I'm focusing my attention on providing users more of what they like.
A few years ago I replaced unhelpful names with more descriptive ones.
Usually Google Guide opens a new browser window when a user clicks on a link outside of Google Guide.
I initially wrote Google Guide in HTML. Jerry Peek and I are translating Google Guide into DocBook.
I noticed that users were choosing the Google Guide Stock Quotes page after entering the query [ Google stock symbol ].
So I added, at the top of the page,
Looking for Google's stock symbol? It's GOOG on Nasdaq. Click here for Google's stock price or search for it on Google.
When putting together content for this page, I came across wonderful pages on creating content for websites, including:
When these people run vanity searches, i.e., search for themselves, they may run across your page and get in touch with you.
At the 30th Asilomar Microcomputer Workshop in 2004, Bill Cheswick suggested this approach to searching for people if you don't find them in Google's phonebook.
| Developing Links to Google Search Results |
If you know HTML, it's relatively easy to make links to Google's search results. Following each link in the examples below is the code that produces it.
Note: The URL — that is, the text shown in Italics here: href="http://URL-GOES-HERE" — must be valid. For instance:
For example, the query [ "a song for you" ] would be encoded in a URL as https://www.google.com/search?q=%22a+song+for+you%22, where each quote (") is replaced by %22.
The easiest way to find the correct encoding is to type your query into a Google Search box — run the search and look at the resulting URL in your web browser's address box (which is usually in the toolbar at the top of the window). Then copy and paste the parts you need from the URL into your HTML code.
With AdSense for Search, you can easily create a revenue stream at the same time as provide a Google search box like the following.
Fill the search box with a query by specifying a value the attribute "value", which AdSense for Search initializes to the null string ("").
Note: If you fill the search box with a query, Google may not share revenue with you.
Note: AdSense for Search centers the search box on the page while AdSense for WebSearch+SiteSearch doesn't. Of course, you can modify the AdSense code to place the search box wherever you want on the page.
| Getting Your Website Listed on Google |
How does Google find your site and list it? Merely registering your domain on the Internet isn't enough.
As soon as your site is available on the Internet, you can submit it to Google by completing the add URL form at www.google.com/addurl.html.
Another way to be listed — and to raise your PageRank too — is by getting other websites to link to yours. After that, when Google's robots or spiders, known as Googlebot, crawl the web, they should run across your site within a month or so. As we mentioned in the How Google Works page, there are two types of crawls, fresh crawls and deep crawls. Your site most likely will first get a fresh crawl in which only pages Google deems most important are crawled. After Google runs a deep crawl of your site, most, if not all of the pages on your website that contain links from other pages will be crawled and subsequently listed on Google — except pages that are included in the file robots.txt, which lists pages that you don't want Google to crawl and pages containing code that Google is unable to parse.
Recently Google developed Google Base, a service, like a bulletin board, for posting all types of content, e.g., coupons, reviews, jobs, housing, events, tickets, merchandise. Things for sale may get cross posted on Froogle and locations may get cross posted from Google Base to Google Maps.
For more about how to get your site listed on Google, visit www.google.com/webmasters/1.html.
How can you remove websites, individual pages, cached pages, and outdated or dead links from Google's index? Visit www.google.com/webmasters/remove.html.
| What's PageRank? |
PageRank is Google's system for ranking web pages. A page with a higher PageRank is deemed more important and is more likely to be listed above a page with a lower PageRank.
Google describes PageRank:
In other words, Google conducts "elections" in which each web page casts votes for web pages with hyperlinks to those pages. But unlike a democracy a page can have more than one vote and links from pages with high PageRank are given more weight (according to their ranking) and thus help to improve the targets' PageRank.
If you don't want a link to be considered for the purposes of PageRank, e.g., a spammer posts a link to a discount pharmacy site, specify the hyperlink attribute rel="nofollow", which Google implemented in January 2005.
See the PageRank of a page with the PageRank meter in the Google Toolbar (an advanced feature). The more green the higher the PageRank.
Compare the relative PageRank of your site with those of other related sites by viewing the green bar to the left of a website in the web page section (near the bottom of the page) of the Google Directory page. (If your site isn't listed in the Directory, that's another way to improve its PageRank. See www.dmoz.org/add.html.)
In the next section, Improving Your PageRank, I offer suggestions for how to improve the PageRank of your webpages.
| Improving Your Website's PageRank |
Below are suggestions for publicizing your site based on our experience getting the word out about Google Guide.
Post your site's URL (web address) to popular web directories including Open Directory Project (ODP), Yahoo!, and LookSmart. Also post your URL to online reference, e.g., Wikipedia, industry-specific expert sites, blogs, etc.
In addition to making it easy for other sites to distribute your headlines and content, your RSS feed will be indexed by popular Blog search engines, including Technorati, BlogSearch, and Ask.com Bloglines.
Note: If your site links to delisted websites, your website might also be removed from Google's index.
Note: If Google suspects that you've traded links with other sites for the sole purpose of improving your ranking, it might penalize or blacklist your site.
Next I emailed journalists who specialize in search engines, but again few wrote articles about Google Guide.
Then I emailed reviewers of books on using Google. A handful responded. Some wrote that Google Guide was for novices; others wrote that Google Guide was tailored for advanced users. Wanting to make Google Guide appeal to novices and experts alike, I indicated sections that would appeal to particular users, e.g.,
After several months of emailing potential users and posting to websites, libraries, schools, and users began linking to Google Guide.
I tried again to get national press coverage by contacting John Markoff from the New York Times. After a few attempts, I was quoted in an article about Search Engine Wars and afterwards Google Guide got over 50,000 unique visitors/day for the following week and traffic has been good ever since.
On the basis of a suggestion from Matt Vance, I created the Google Guide Cheat Sheet and announced it on Slashdot, which generated great publicity, along with a few flames; within 24 hours, the Cheat Sheet went from being ranked so poorly I couldn't even find it to being ranked #2 (after Google's cheat sheet).
Recently Google Guide was translated into Hebrew.
When I first made this site publicly available, Google Guide wasn't in the first 100 sites on searches for [ Google guide ]. Thanks to the sites that linked to Google Guide and users who clicked on Google Guide in their search results, Google Guide is in the top ten results for many queries that relate to the content of the site. Being listed so highly on Google has improved the traffic flow to Google Guide.
Note: For the top ranked site, Google sometimes includes useful links from within that site.
Google Guide
Interactive online tutorial on using the search engine includes tips and information on new services...
classic.googleguide.com/ - 7k -Cached - Similar pages
Query Input - Special Tools
Introduction - Understanding Results
More results from classic.googleguide.com
In addition to considering the number of links to your page and the ranking of the linking page, to compute a page's PageRank, Google considers hundreds of factors including
These factors and many others are described in the article "Great Site Ranking in Google The Secret's Out" on Buzzle.com.
Google periodically changes how it calculates a page's importance, thereby resulting in shifts in rankings, known as a Google Dance. Google Guide's placement in Google's search results sometimes changes when Google modifies or enhances their indexing algorithms.
I don't try to keep up with the latest search engine optimization tricks. Instead I strive to make searching Google easier by educating users about Google services, capabilities, and features. When I am successful, sites link to Google Guide pages and increase their ranks and importance to Google.
Here are links to a few pages that discuss how to publicize your website and improve the ranking of your web pages.
In the next section, Advertising Your Website, I'll tell you how I increase traffic through running inexpensive ads.
| Advertising Your Website |
To increase traffic and to learn about Google's advertising services, I became an AdWords advertiser. I designed simple text ads, chose queries and keywords the ads should match, and specified the maximum we were willing to spend on an advertising campaign. Google charges us only when someone clicks on one of our ads.
AdWords contributes greatly to Google's bottom line, i.e., it's profits. Google offers many resources to educate website owners about AdWords. Rather than developing tutorial material on AdWords, which is likely to get outdated when Google enhances AdWords capabilities and features, I encourage you to learn from Google's material and those of third parties.
We increased the effectiveness of our advertising by following wonderful suggestions from Perry Marshall's free 5-day course and from his Definitive Guide to Google AdWords, which you can learn about at www.perrymarshall.com/google/. We tested lots of ads targeted on many different queries and keywords until we found ones that got favorable responses from users, i.e., the ads that users clicked on. And Google has rewarded us by overrunning our ads, i.e., showing some of them from time to time at no cost to us.
Now that Google Guide gets thousands of unique visitors each day most of whom find the site via a Google Search, I've stopped running ads, but Google is saving our ads and campaigns in case I decide to run them again.
| Generating Revenue by Running Ads on Your Website |
You can make money from Google AdSense by hosting
Display ads that it deems relevant to the content of the page.
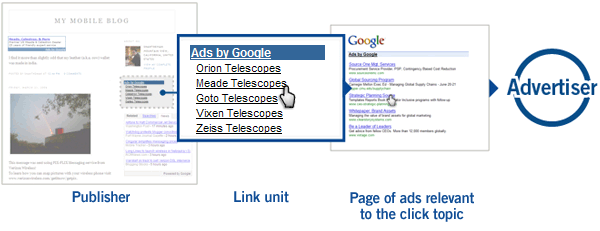
Display a list of topics that Google deems relevant to the content of the page.
A page of related ads is displayed when a user clicks on a topic.
Provide web search and earn revenue from Google.
Generate revenue by providing a query box for searching the web and the specific site(s) of your choice.
Generate income by referring your users to Google products and search services.
At first I was reluctant to run ads on Google Guide. I didn't want to create any distractions that would lure visitors away from my site. But visitors leave even if I don't run ads. So I ran ads at the bottom of a page because I thought they would distract only viewers who weren't interested in my site. Few users clicked on the ads. Later I moved the ads to the top of a page. The response rate more than doubled and so did revenue.
Why did Google create AdSense? Many sites wanted to advertise and Google wanted more real estate, i.e., web pages, on which it could display ads. Web sites wanted a slice of Google's revenue.AdSense is a money-generating service for Google and it's users. Unlike user services, Google provides a wealth of resources on AdSense, just a few of which I've listed below.
| [Home] [Intro] [Contents] [Print] [Favorites] [Query Input] [Understanding Results] [Special Tools] [Developing a Website] [Appendix] |
|
For Google tips, tricks, & how Google works, visit
Google Guide at classic.GoogleGuide.com. By Nancy Blachman and Jerry Peek who aren't Google employees. For permission to copy & create derivative works, visit Google Guide's Creative Commons License webpage. |